-
Growth rate set to slow to 16-year low of 3.3% as oil falls
-
Naira policy is biggest concern, Citigroup analyst Howell says
ability to turn around Africa’s largest economy and oil producer.
Money that flowed into stocks and bonds in the West African nation, which McKinsey & Co. says could become one of the world’s 20 biggest economies by 2030, is now fleeing as growth prospects diminish along with oil prices. While Buhari, 72, has prioritized stamping out the graft that has plagued Nigeria since independence from Britain in 1960, policy-making appears as uncertain and haphazard as ever.
“After the initial euphoria, people have become disillusioned,” Ayodele Salami, who oversees about $500 million of African equities as chief investment officer of London-based Duet Asset Management Ltd., said by phone. “He would probably say that he’s being deliberative and cautious. But we expected more.” Duet’s Africa fund has cut its investments in the country to about 24 percent of the total from 38 percent in the last year.
Buhari waited five months before naming his cabinet, hasn’t proposed a clear plan to revive growth and backed foreign-exchange controls aimed at defending the naira. His retention of gasoline subsidies, plans to raise spending in the face of declining revenue and silence about a $5.2 billion fine levied on mobile-phone operator MTN Group Ltd. have added to investor unease.
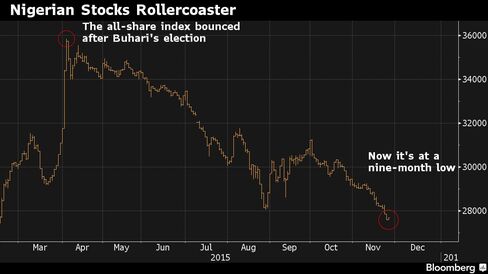
Nigeria’s benchmark stock index has plunged 22 percent since reaching a year-high on April 2, the day after Buhari was declared the winner of the presidential race against incumbent Goodluck Jonathan. That’s the third-worst performance globally in the period, after the bourses in Ukraine and Egypt. The index advanced 12.5 percent in the two days after Jonathan conceded.
Garba Shehu, a spokesman for Buhari, didn’t immediately respond to written questions after requesting they be sent that way.
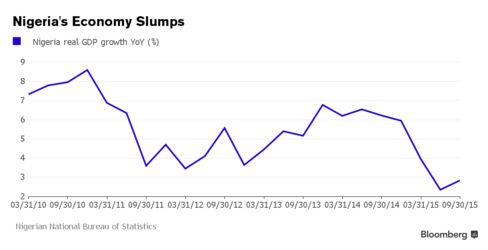
The hiatus has compounded the pain caused by the slide in the price of crude, which accounts for two-thirds of government revenue and 90 percent of export earnings. Growth, which averaged 6.3 percent annually over the past decade, is set to slow to a 16-year low of 3.3 percent this year, according to the median estimate of 15 economists surveyed by Bloomberg.
Many filling stations ran dry this month as the government withheld fuel subsidies to suppliers, preventing them from restocking. Lengthening lines forced Buhari to ask lawmakers for permission to pay 413 billion naira ($2 billion) in overdue payments, an amount that hadn’t been budgeted for.
While next year’s budget has yet to be finalized, Buhari wants to raise spending by 56 percent, according to a person who attended a briefing on the government’s plans and asked not to be identified because the matter is private. Vice President Yemi Osinbajo says the government plans to spend its way out of a slowing economy and that an infrastructure fund will be created with public and private financing.
“You cannot deny there might be a fiscal element to the massive fine,” he said by phone from Paarl, near Cape Town. “It will make investors a little bit more wary of investing in Nigeria.”
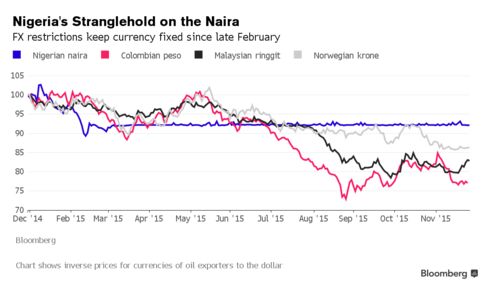
An even bigger concern for many investors is the authorities’ naira policy. The Central Bank of Nigeria, with Buhari’s backing, has burned through $4.3 billion of reserves this year and choked off supply of foreign exchange to banks and their customers to defend the naira, even as major oil exporters such as Russia and Colombia have let their currencies slide. The restrictions prompted JPMorgan Chase & Co. to remove Nigeria from its local-currency emerging-market bond indexes, tracked by more than $200 billion of funds, in September, triggering a selloff in the nations’ assets.
While the naira has been all but fixed at about 198 to 199 per dollar since March, forward prices suggest it will drop by almost one-fifth, to 243.5, in a year.
Nigerian Breweries Plc, the nation’s biggest brewer, controlled by Heineken NV, said it takes two weeks to obtain dollars to pay for its imports, twice as long as it took a few months ago.
Buhari has won plaudits from leaders including President Barack Obama for his efforts to tackle graft. He replaced the management of the state oil company, which was accused of withholding billions of dollars from the government, and has stepped up the fight against an insurgency being waged by Islamist group Boko Haram.
“The degree of transparency we’re starting to get with the new administration is hugely positive,” Douglas Rowlings, an analyst at Moody’s Investors Service, said in an interview in Lagos. “It gives investors the perception that operating in Nigeria will now be done following proper procedures.”
Jan Dehn, head of research at Ashmore Group Plc, which oversees almost $60 billion of emerging market assets, remains unconvinced that Buhari is up to the job. The fund manager sold all its Nigerian government debt in the past year.
“So far the Buhari administration has done all the wrong things,” Dehn said by phone from London. “Not only has he been incredibly slow in taking any action, when he finally has taken action on the economic front it’s been diametrically opposed to sensible policy. That is a major disappointment given expectations prior to his election.”
No comments:
Post a Comment